Humanoid Robots: The Next Evolution of Automation and the Future of Human–Machine Collaboration (2025 Edition)



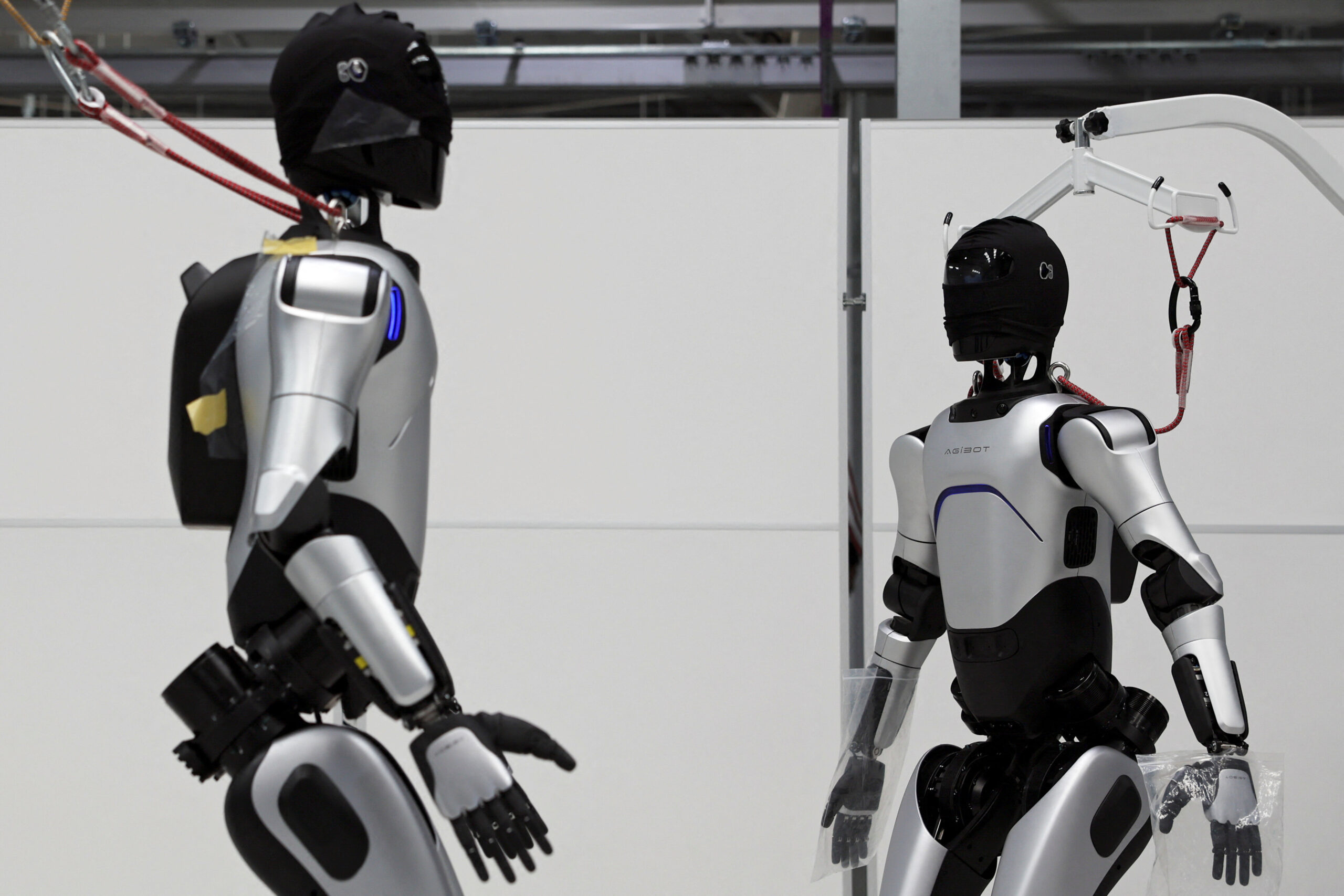
Humanoid robots—machines designed to look and move like humans—are no longer distant science fiction. In 2025, rapid developments in artificial intelligence, mechanical engineering, materials science, and sensor technology are turning humanoid robots into practical workers. They can walk, grasp objects, interact with humans, learn tasks, and assist in homes, hospitals, and industries.
For decades, robotics companies dreamed of creating machines capable of navigating human environments without needing specialized spaces. Today, that dream is closer than ever to reality. Humanoid robots are stepping into roles once considered too complex for autonomous machines. Their ability to operate tools, climb stairs, lift objects, and perform routine tasks positions them as one of the most transformative technologies of the decade.
This article explores what humanoid robots are, how they work, recent breakthroughs, real-world use cases, industry adoption, benefits, challenges, and the future of human–robot collaboration.
What Are Humanoid Robots?
Humanoid robots are robots designed with a human-like shape, typically featuring:
- A head
- Torso
- Two arms
- Two legs (or wheels in some models)
- Human-like joints and movement capabilities
Their purpose is not just to look human, but to perform tasks in environments designed for humans. This includes homes, warehouses, stores, hospitals, factories, and offices—places built around human height, dexterity, and mobility.
Humanoid robots combine robotics engineering with advanced AI, giving them the ability to interact and collaborate with people naturally.
How Humanoid Robots Work



Creating a humanoid robot requires the integration of multiple technologies working seamlessly. Below are the core systems that make these robots possible.
Mechanical Structure
Humanoid robots use a combination of:
- Lightweight alloys
- High-strength plastics
- Carbon fiber
- Hydraulic or electric actuators
These components allow them to mimic human-like movement, balance, and strength.
Actuators and Motors
Actuators act as muscles, enabling robots to:
- Bend
- Lift
- Rotate
- Walk
- Grip objects
Modern robots use high-efficiency electric actuators for quiet, precise movements.
Sensors
Sensors provide perception and awareness. These include:
- Cameras for vision
- LiDAR for mapping
- Infrared sensors
- Touch sensors
- Gyroscopes and accelerometers for balance
AI and Decision-Making
Humanoid robots use artificial intelligence for:
- Task execution
- Object recognition
- Environmental awareness
- Human interaction
- Learning from experience
Large language models (similar to those behind conversational AI) are increasingly integrated into robots for natural communication.
Power Systems
Most humanoid robots run on:
- High-density batteries
- Energy-efficient actuators
- Heat-management systems
Battery life remains a major challenge, but rapid improvements are underway.
Breakthroughs in Humanoid Robotics (2023–2025)
Recent years have produced unprecedented advances, making humanoid robots far more capable and commercially viable.
Natural Walking and Balance
Thanks to advanced control algorithms, robots now:
- Walk on uneven surfaces
- Climb stairs
- Avoid obstacles
- Regain balance after slips
Companies like Boston Dynamics, Tesla, Figure AI, and Agility Robotics have showcased dramatic improvements.
Hand Dexterity and Object Manipulation
Humanoid robots can now:
- Pick up fragile items
- Use tools
- Type on keyboards
- Open doors
- Operate factory equipment
Dexterity was once the biggest barrier. Today, robots can adjust their grip in real time using touch and pressure sensors.
Autonomous Task Learning
With AI agents integrated into robotics systems, humanoid robots can learn new tasks by:
- Watching humans perform actions
- Processing video datasets
- Receiving verbal instructions
- Analyzing step-by-step demonstrations
This dramatically reduces programming requirements.
Lower Production Costs
The development of mass-producible components has lowered costs. Startups are racing to build affordable humanoid robots for businesses.
Types of Humanoid Robots
Different humanoid robots are designed for different uses.
Industrial Humanoids
Used in factories and warehouses. Built for strength, reliability, and repetitive tasks.
Examples:
- Tesla Optimus
- Figure 01
- Agility Robotics’ Digit
Service Robots
Designed for hospitality, retail, and customer service roles.
Examples:
- Softbank Robotics’ Pepper
- UBTECH Walker X
Healthcare and Assistive Robots
Robots helping seniors and people with disabilities through mobility and daily tasks.
Examples:
- Toyota’s Human Support Robot
- Exoskeletons for rehabilitation
Research Humanoids
Built for scientific exploration, human behavior study, and disaster response.
Examples:
- Boston Dynamics Atlas
- NASA’s Valkyrie
Real-World Applications of Humanoid Robots
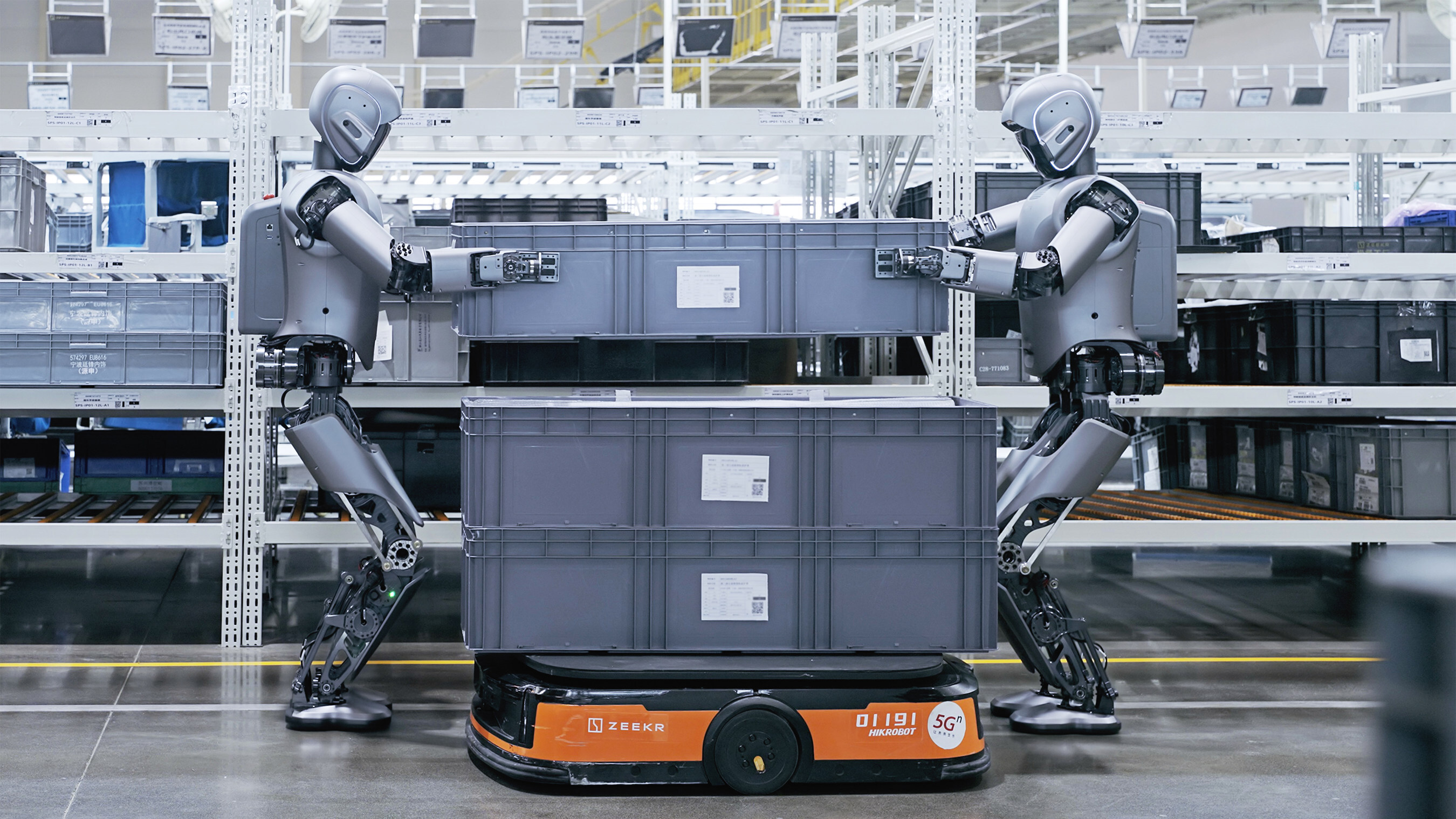



Humanoid robots are beginning to integrate into everyday life and major industries.
Manufacturing and Logistics
Factories are early adopters. Robots can:
- Move inventory
- Assemble components
- Lift heavy items
- Pack and sort materials
- Perform repetitive, ergonomically difficult tasks
The advantage is clear: humanoid robots can use existing human-designed infrastructure without requiring major facility changes.
Retail and Hospitality
Robots are assisting in:
- Greeting customers
- Providing product information
- Cleaning
- Shelf restocking
- Delivering items
Their human-like presence makes interactions more intuitive.
Healthcare
Hospitals use humanoid robots for:
- Patient monitoring
- Delivering medication
- Assisting elderly individuals
- Helping with physical therapy
- Reducing staff workload
Assistive robots support individuals with mobility limitations, helping them live more independently.
Home Assistance
Consumer humanoid robots are emerging slowly but steadily. They may eventually handle:
- Cleaning
- Cooking assistance
- Child monitoring
- Household organization
These robots are still in early stages, but tech companies are investing heavily.
Education
Robots are being used to:
- Tutor children
- Assist in STEM labs
- Demonstrate AI and robotics concepts
- Provide companionship for neurodiverse learners
Public Safety and Disaster Response
Humanoid robots can enter dangerous environments where humans cannot safely operate, such as:
- Fire zones
- Disaster sites
- Radioactive areas
- Collapsed buildings
Their human-like shape allows them to navigate around obstacles in unpredictable environments.
Why Humanoid Robots Matter
Humanoid robots offer several advantages that distinguish them from traditional robots.
Adaptability
They can use objects and tools designed for humans. No redesigning infrastructure.
Mobility
Legged robots can move where wheeled robots cannot. Stairs, slopes, and uneven terrain are manageable.
Human Interaction
Their humanoid form makes communication easier and more natural.
Workforce Support
Robots help solve labor shortages in:
- Manufacturing
- Logistics
- Healthcare
- Construction
They assist, not replace, human workers—handling high-risk or repetitive tasks.
Scalability
Robots can work 24/7 without fatigue, increasing output in critical industries.
Challenges Facing Humanoid Robots


Although progress is rapid, challenges remain.
Battery Life
Most humanoid robots operate for only one to two hours per charge. Research into solid-state batteries and high-density cells is underway.
Cost
Advanced humanoid robots are expensive to build. Mass manufacturing will lower costs over time.
Movement Speed
Robots walk slower than humans due to safety constraints and limited actuator power.
Safety
Working around humans requires advanced safety systems to prevent injuries.
Dexterity Limits
Humans still outperform robots in delicate, high-precision tasks.
Ethical and Social Acceptance
Concerns include:
- Job displacement
- Overdependence on robots
- Privacy
- Social interaction changes
These must be addressed responsibly.
Key Companies Leading Humanoid Robotics (2025)
The humanoid robot industry is led by several pioneering companies making major strides.
Tesla – Optimus
Focuses on factory work, household tasks, and scalable production.
Figure AI – Figure 01
A full-scale humanoid robot designed for manufacturing and logistics.
Boston Dynamics – Atlas
Known for advanced mobility, parkour, jumping, and agility.
Agility Robotics – Digit
A bipedal warehouse robot used for stock movement.
UBTECH Robotics – Walker X
A humanoid home and service robot.
Sanctuary AI – Phoenix
Focused on cognitive robotics with strong AI capabilities.
RobotEra, Engineered Arts, and Others
Focused on entertainment, education, and human interaction.
Future of Humanoid Robots (2025–2040)



Humanoid robots will evolve dramatically in the next 10 to 15 years.
Factory and Warehouse Integration
By 2030, thousands of humanoid robots will likely work in factories worldwide.
Household Robots
Consumer robots capable of laundry, cooking assistance, and cleaning will emerge mid-2030s.
Healthcare Expansion
Robots will support:
- Elder care
- Rehabilitation
- Hospital logistics
- Remote surgeries
Full Autonomy
Future humanoids will navigate environments with little human oversight.
Learning from Video
Robots may learn tasks by watching online videos, just like humans observe tutorials.
Emotional Intelligence
AI advancements will enable robots to detect and respond to human emotions.
Human Augmentation
Some humanoids may serve as physical extensions of humans, controlled by BCIs or remote operators.
Impact of Humanoid Robots on Society
Humanoid robots will influence nearly every part of modern life.
Economic Impact
They will boost productivity in factories, logistics, and customer service.
Workforce Transformation
Humans will shift to creative, supervisory, and strategic roles.
Improved Quality of Life
Elderly and disabled individuals will gain more independence.
Education Innovation
Robots will act as tutors and learning assistants.
Ethical Considerations
Society must develop policies for:
- Privacy
- Safety
- Responsible automation
- Fair workforce transition
Proper governance is essential as these machines become more common.
Conclusion
Humanoid robots represent one of the most important technological revolutions of the 21st century. They merge artificial intelligence with physical capability, creating machines that can assist humans across industries—from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare, hospitality, and home life.
While challenges remain, progress between 2023 and 2025 demonstrates that humanoid robots are advancing faster than almost any other technology. As their cost decreases and capabilities expand, these robots will become commonplace, reshaping how we live and work.
Humanoid robots are not just a technological innovation—they are the next stage of human–machine collaboration.