Sustainable Energy Technologies: The Innovations Powering a Cleaner, Greener Future (2025 Edition)



Sustainable energy technologies are transforming the global energy landscape. As climate change accelerates and fossil fuel challenges intensify, nations, cities, and industries are turning to renewable energy systems and high-efficiency technologies that promise both environmental sustainability and long-term economic resilience.
In 2025, sustainable energy is no longer an idealistic vision—it is an active global priority. Breakthroughs in solar energy, wind power, green hydrogen, energy storage, smart grids, geothermal systems, sustainable fuels, and carbon capture are redefining how we power homes, industries, and transportation.
This article explores the latest sustainable energy technologies shaping 2025 and beyond, explaining how they work, why they matter, the breakthroughs powering their growth, and their potential impact on the planet.
What Is Sustainable Energy?
Sustainable energy refers to energy sources and technologies that:
- Do not deplete natural resources
- Produce little or no greenhouse gas emissions
- Support long-term environmental balance
- Remain economical and scalable
- Are renewable or regenerative
Key categories of sustainable energy include:
- Solar
- Wind
- Hydropower
- Geothermal
- Biomass
- Tidal and wave energy
- Hydrogen
- Energy storage systems
- Carbon capture and utilization
The goal is to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and move toward a clean, stable, global energy system.
Why Sustainable Energy Matters Today
Sustainable energy technologies address urgent global challenges:
Climate Change
Clean energy reduces greenhouse gases responsible for global warming.
Energy Security
Nations with renewable infrastructure reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Economic Growth
Green technologies create millions of jobs across construction, manufacturing, and innovation.
Health Benefits
Cleaner air reduces respiratory diseases and premature deaths.
Long-Term Stability
Renewable resources like sunlight and wind are virtually limitless.
This transition is not only environmental—it is economic, political, and societal.
Major Sustainable Energy Technologies Transforming 2025
Below are the leading sustainable technologies driving global energy progress.
Solar Power Technologies
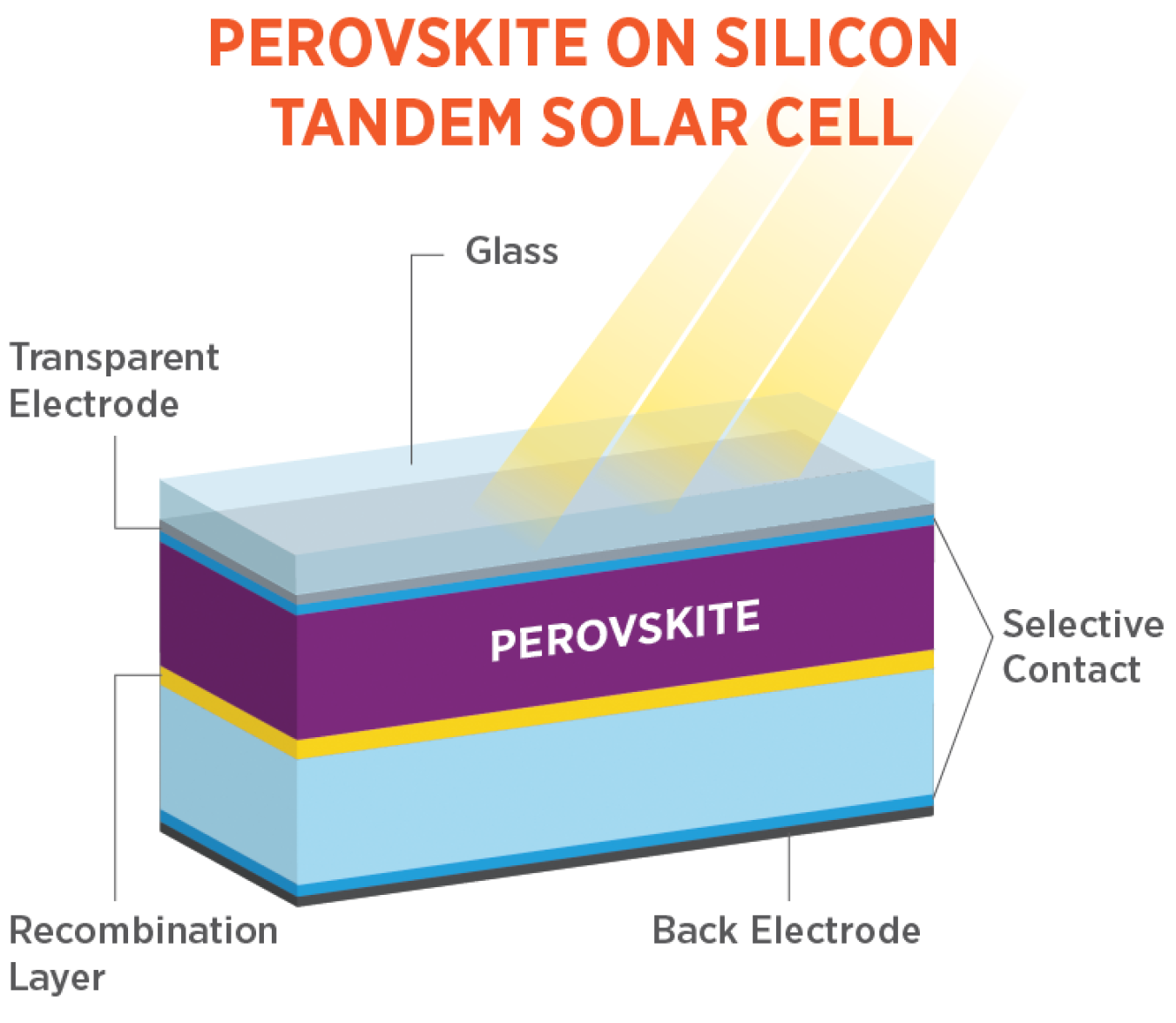


Solar power remains the world’s fastest-growing clean energy source, supported by declining costs and technological breakthroughs.
Perovskite Solar Cells
One of the most promising innovations, perovskites offer:
- Higher efficiency than silicon
- Lower manufacturing costs
- Flexible, lightweight designs
Efficiency rates have surpassed 30%, making them a future industry standard.
Bifacial Solar Panels
Capture sunlight on both sides, improving performance by up to 30%.
Transparent Solar Panels
Windows that double as energy-generating surfaces.
Solar Roof Tiles
Integrated solar material blends with building design.
Solar Thermophotovoltaics
Converts heat into electricity with extremely high efficiency.
Solar innovations are making energy generation cheaper, more efficient, and more visually seamless.
Wind Power Innovations

4
Wind technology remains a cornerstone of sustainable energy.
Offshore Wind Farms
Offshore wind turbines generate more power due to stronger, steadier winds.
Floating Wind Turbines
Mounted on floating platforms for deep-ocean installation.
Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)
Compact, quiet, and ideal for urban environments.
Airborne Wind Turbines
Drones or kites fly high in the atmosphere to capture stronger wind currents.
Super-Turbines
Next-generation towers reach heights above 300 meters to maximize output.
Wind power continues to expand its global footprint with innovations improving efficiency and location flexibility.
Energy Storage Technologies


4
Energy storage is essential for stabilizing renewable power.
Lithium-Ion Advancements
Safer, longer-lasting models with faster charging.
Solid-State Batteries
Higher energy density, lower fire risk, and longer lifespan.
Flow Batteries
Large-scale storage using tanks of electrolyte solutions.
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Stores wind or solar power by compressing air underground.
Thermal Energy Storage
Stores heat or cold, then converts it to energy when needed.
Gravity-Based Storage
Uses heavy blocks in towers to store and release energy.
As renewable adoption grows, energy storage becomes a foundational technology for modern power grids.
Green Hydrogen
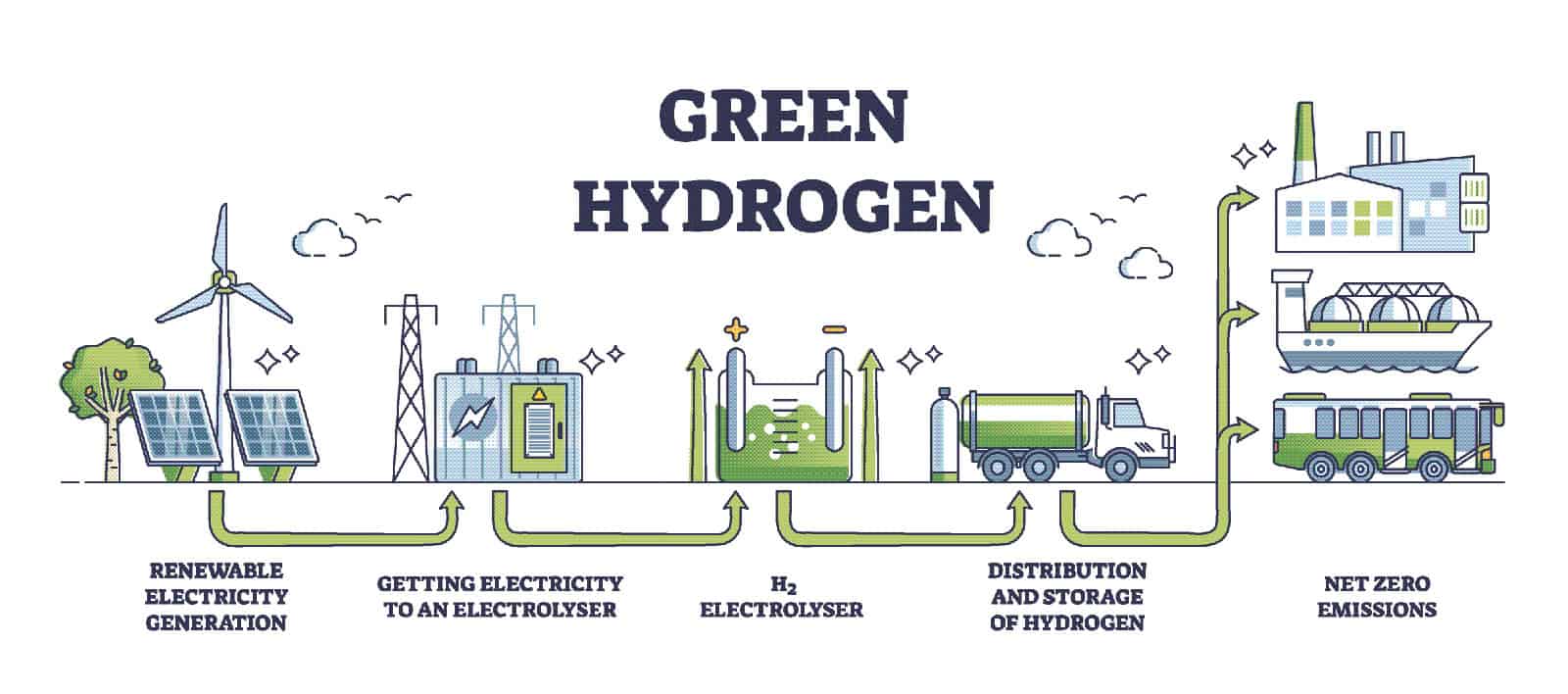


Green hydrogen—produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy—is becoming a major player in clean energy.
How It Works
Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity from:
- Solar
- Wind
- Geothermal
Applications
- Industrial fuel
- Steel and cement production
- Aviation
- Long-duration energy storage
- Heavy transport systems
- Heating
Breakthroughs
New electrolyzers reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Hydrogen pipelines and storage networks are under development globally.
Green hydrogen is crucial for decarbonizing industries that cannot electrify easily.
Geothermal Energy

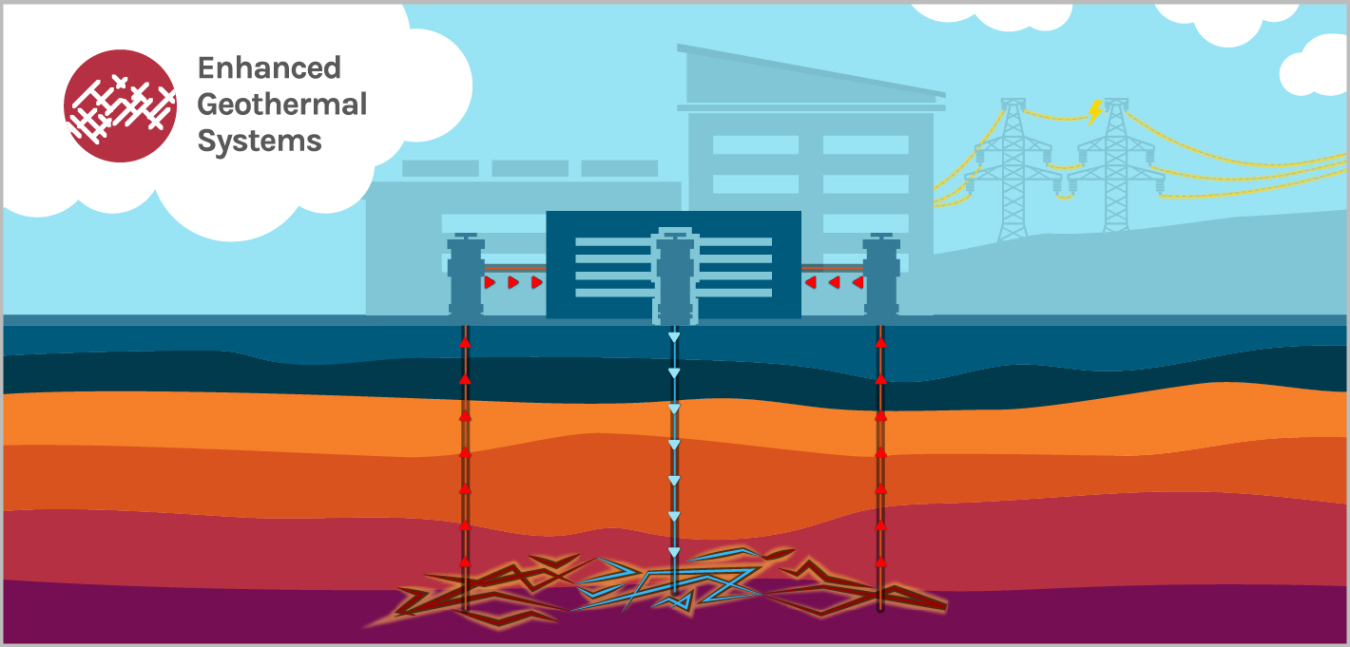
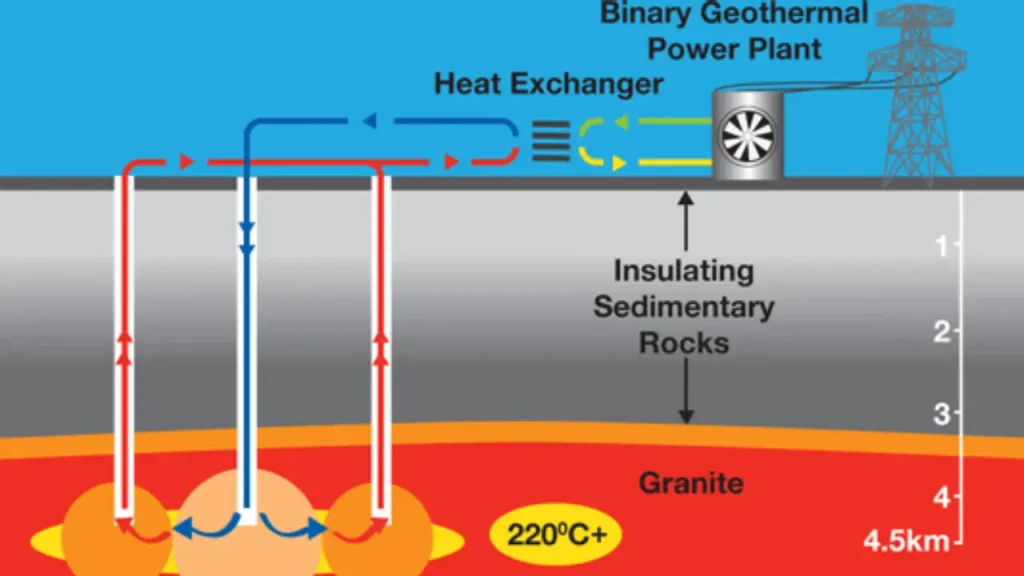
Geothermal energy taps into Earth’s natural heat.
Traditional Geothermal
Uses underground heat to produce steam and generate electricity.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS)
Uses drilling and fluid injection to create artificial geothermal reservoirs.
Unlocks geothermal power in regions previously unusable.
Direct Heating and Cooling
Geothermal heat pumps provide efficient temperature control for homes and businesses.
Supercritical Geothermal
Targets extremely high-temperature zones for massive energy output.
With new drilling technologies, geothermal is becoming a reliable 24/7 sustainable energy source.
Hydropower and Marine Energy



Hydropower is one of the oldest renewable energy sources—but innovation continues.
Small-Scale Hydropower
Environmentally friendly micro-turbines power remote communities.
Tidal Energy
Harnesses predictable ocean tides with underwater turbines.
Wave Energy
Captures surface wave motion for electricity generation.
Pumped-Storage Hydropower
Acts like a giant battery, storing energy for grid balancing.
Marine energy is consistent and predictable, making it a strong complement to solar and wind.
Bioenergy and Sustainable Fuels


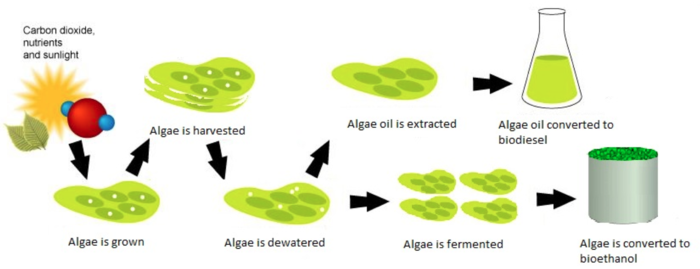
Bioenergy taps into biological material for clean energy.
Biomass Power
Converts organic materials into electricity or heat.
Biofuels
Sustainable fuels for aviation, shipping, and transportation.
Algae-Based Fuels
High-yield, low-footprint biofuel production method.
Biogas
Anaerobic digestion converts organic waste into renewable methane.
Bioenergy supports circular economies and reduces landfill and agricultural waste.
Smart Grids and AI-Powered Energy Systems


Smart grids use digital communication, sensors, and automation to enhance energy systems.
AI for Load Balancing
Artificial intelligence predicts energy demand and manages fluctuating supply.
Smart Meters
Give real-time insights for consumers and utilities.
Grid Decentralization
Renewable microgrids increase resilience.
Demand Response Programs
Automatically adjust energy usage to reduce waste and lower costs.
Smart grids are essential for harmonizing the variability of solar and wind power.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)



CCUS technologies capture carbon dioxide from industrial sources or the air, then store or repurpose it.
Direct Air Capture
Removes CO₂ directly from the atmosphere.
Carbon Mineralization
Turns CO₂ into stable minerals like carbonates.
Industrial Capture
Captures emissions from factories and power plants.
Carbon Utilization
Uses captured carbon to produce:
- Fuels
- Concrete
- Plastics
- Building materials
CCUS plays a critical role in achieving net-zero emissions.
Fusion Energy and Next-Gen Nuclear
Though technically not “renewable,” next-generation nuclear and fusion are sustainable due to low emissions and long-term fuel availability.
Fusion Energy
Mimics the reaction that powers the sun.
Breakthroughs since 2022 show strong potential for the 2030s.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
Safer, compact nuclear reactors suitable for cities and remote areas.
These technologies will help meet global baseload energy demands sustainably.
Barriers and Challenges in Sustainable Energy


Despite rapid progress, challenges remain:
Intermittency
Solar and wind require strong energy storage to ensure 24/7 power.
High Initial Costs
Infrastructure investments can be expensive.
Land and Resource Requirements
Solar farms, wind farms, and hydro projects need significant space.
Grid Limitations
Aging grids struggle to support modern renewable integration.
Material Supply Chains
Batteries need lithium, cobalt, and rare metals.
Permitting and Policy
Construction delays often result from complex regulations.
Solutions are emerging, but global coordination is needed.
The Future of Sustainable Energy (2025–2050)



The next decades promise dramatic advancements:
Complete Decarbonization of Power Grids
Major countries will shift toward 100% clean energy.
Electrification of Transportation
EVs, hydrogen vehicles, electric aviation, and autonomous delivery systems.
Smart Cities
AI-driven energy optimization for buildings, transportation, and services.
Cheap Renewable Power
Solar and wind may become the lowest-cost energy sources worldwide.
Global Hydrogen Economies
Hydrogen hubs for industry, transport, and storage.
Space-Based Solar Power
Orbiting solar station concepts will collect energy and beam it to Earth.
Energy Democracy
Communities produce their own energy via microgrids.
Sustainable energy will eventually power every major sector of society.
Conclusion
Sustainable energy technologies are redefining global power systems and enabling a cleaner, healthier, and more resilient world. From solar breakthroughs and advanced batteries to green hydrogen, tidal energy, geothermal systems, and AI-driven smart grids, the innovations of 2025 show that a truly sustainable future is no longer theoretical—it is already emerging.
These technologies not only reduce emissions but create new industries, support millions of jobs, enhance energy security, and improve the quality of life across the globe. As investments increase and scientific breakthroughs accelerate, the world is steadily moving toward a carbon-neutral future powered by renewables and sustainable energy systems.
Sustainable energy is not just the future—it is the foundation of a thriving 21st-century civilization.