Quantum Computing: The Next Leap in Computational Power and the Technology That Will Redefine the Future (2025 Edition)


Quantum computing has moved from theoretical speculation to one of the most groundbreaking technological advancements of the 21st century. In 2025, this rapidly evolving field is transitioning from research labs into real-world applications, solving problems that classical computers — even the most powerful supercomputers — cannot handle.
This technology will reshape industries such as cybersecurity, medicine, finance, climate modeling, artificial intelligence, and materials science. Understanding quantum computing today is like understanding the internet in the early 1990s: those who learn it early will be ahead of the next technological revolution.
In this in-depth article, we explore what quantum computing is, how it works, the breakthroughs happening today, the industries it’s transforming, and the challenges that must be solved before mass adoption.
This 1500+ word guide is an essential resource for students, tech professionals, business owners, and anyone who wants to understand the future of computing.
What Is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a revolutionary computing method that uses the principles of quantum mechanics — the physics that governs atoms and subatomic particles — to process information.
While traditional computers use bits to represent information as 0 or 1, quantum computers use qubits, which can be:
- 0
- 1
- and both 0 and 1 at the same time
This ability is called superposition, and it gives quantum computers enormous computational power far beyond anything possible with today’s machines.
Why Classical Computers Fall Short
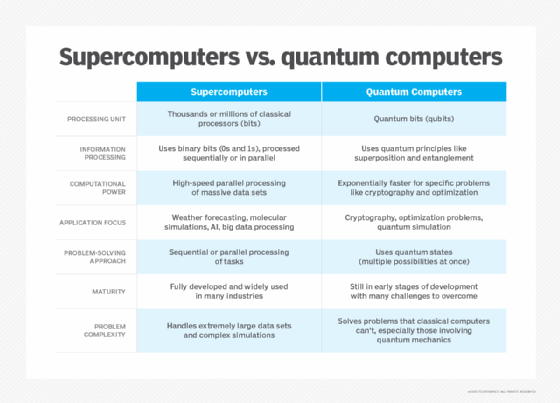
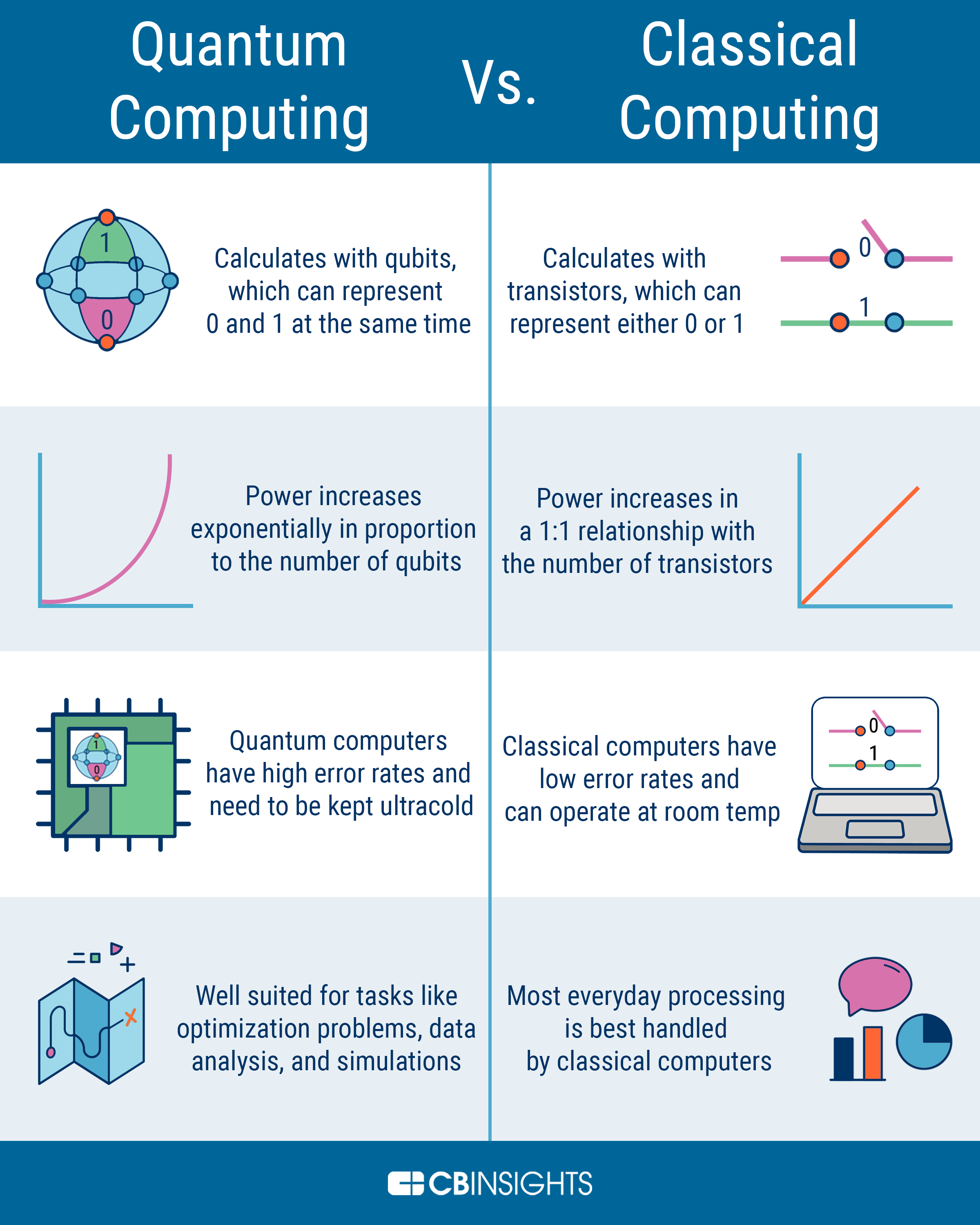

Today’s computers — even supercomputers — operate on strict binary logic:
- A transistor is ON (1)
- Or OFF (0)
They perform calculations sequentially or in parallel, but they cannot escape the binary limits of physical transistor design.
As problems become more complex — such as simulating molecules, optimizing global supply chains, or modeling weather patterns — the computational requirements grow exponentially.
Example:
A classical computer trying to simulate a caffeine molecule needs billions of processing steps. A quantum computer could simulate it instantly.
The world needs new computational processes — and quantum computing offers the leap forward.
The Principles Behind Quantum Computing
Quantum computers rely on three major principles of quantum mechanics:
1. Superposition
A qubit can be in multiple states at once.
Instead of being either 0 or 1, it can be:
- 0
- 1
- 0 and 1 simultaneously
This allows quantum computers to process many possibilities at the same time, unlocking exponential computational power.
2. Entanglement
Entangled qubits become connected so that:
- Changing the state of one instantly affects the other
- Even if they are miles apart
Entanglement gives quantum computers the ability to correlate qubits in ways classical systems cannot, increasing speed and efficiency.
3. Quantum Interference
Quantum computers use interference to amplify correct answers and cancel out incorrect ones.
This property allows quantum algorithms to find optimal solutions extremely quickly.
How Do Quantum Computers Work?



Quantum computers consist of several components:
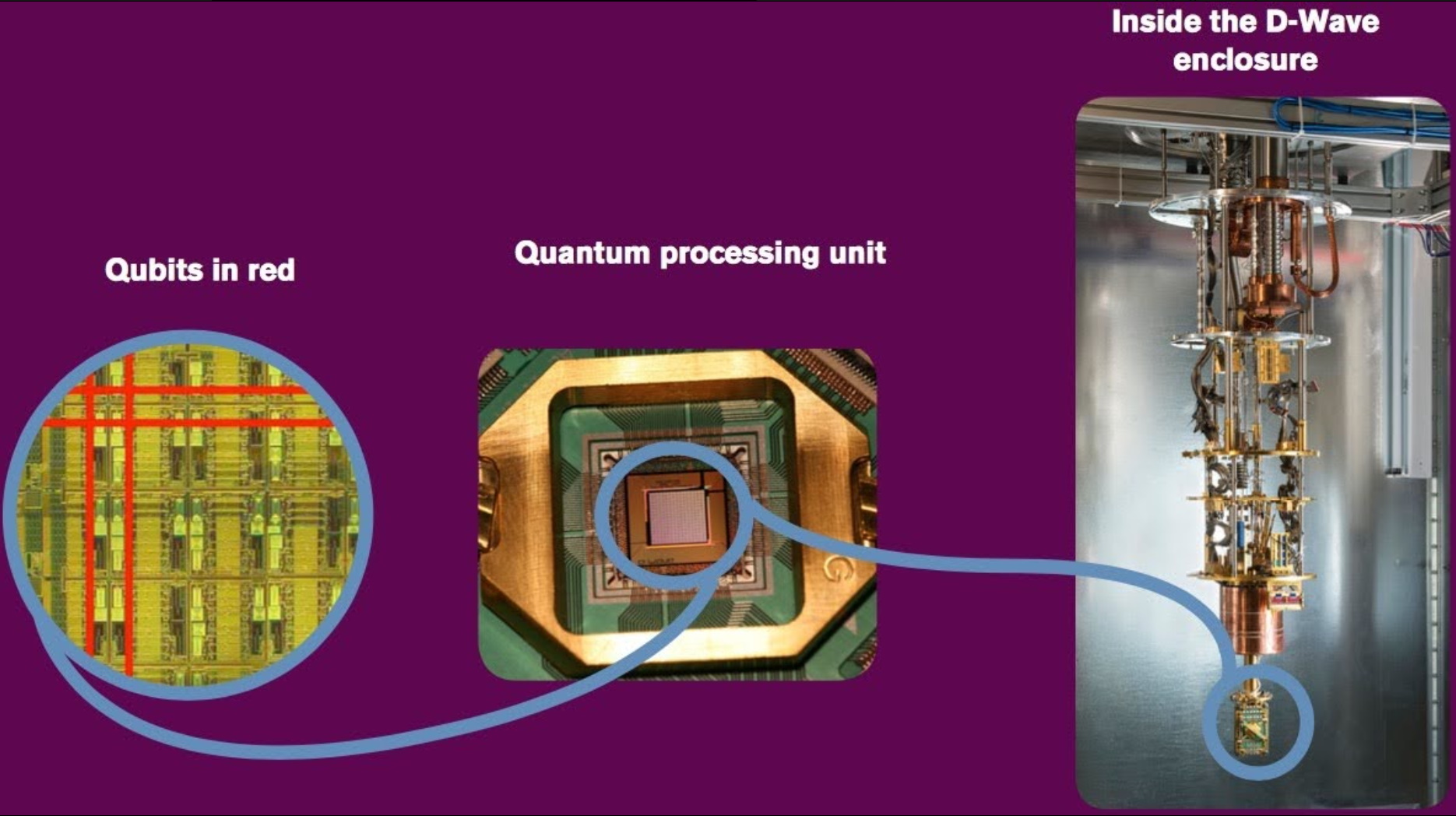
1. Qubits
Physical embodiments of quantum information.
Common types include:
- Superconducting qubits (used by Google, IBM)
- Photonic qubits
- Trapped ions
- Topological qubits
- Neutral atoms
2. Quantum Gates
Like logic gates in classical computers, but they manipulate qubits using:
- Lasers
- Microwaves
- Magnetic fields
3. Quantum Circuits
Sequences of quantum gates that perform computations.
4. Cryogenic Refrigeration
Most quantum computers must be kept near absolute zero (-273°C) to remain stable.
5. Error Correction Systems
Quantum data is extremely fragile.
Noise, heat, and even cosmic rays can cause errors.
Quantum Error Correction (QEC) is one of the biggest challenges in the industry.
Recent Breakthroughs: Why 2025 Is a Turning Point
The last three years witnessed milestones that moved quantum computing from theory toward practical use. These breakthroughs changed everything:
1. Error Rate Reduction
Quantum systems now have dramatically lower error rates thanks to:
- New materials
- Improved qubit design
- Advanced cooling systems
- Better isolation
This increases computation stability.
2. Quantum Machines Reaching “Utility Scale”
IBM, Google, and startups like Quantinuum and PsiQuantum have built quantum processors with:
- More than 1000 qubits
- Coherence times long enough for multi-step calculations
- Hybrid computing platforms
This is the first time quantum machines can solve real problems.
3. Quantum-Classical Hybrid Models
Companies are building systems where:
- Classical computers handle large-scale data
- Quantum machines handle optimization or simulation tasks
This hybrid approach accelerates adoption across industries.
4. Photonic and Neutral Atom Quantum Computing
Startups like Xanadu and Atom Computing are proving that qubits can be:
- Room-temperature
- Highly scalable
- More stable
These alternative architectures may replace current superconducting models.
5. Cloud Quantum Computing
Platforms like:
- IBM Quantum
- Amazon Braket
- Microsoft Azure Quantum
allow developers to build quantum programs without owning a physical machine.
This makes quantum computing more accessible than ever.
What Quantum Computers Will Transform

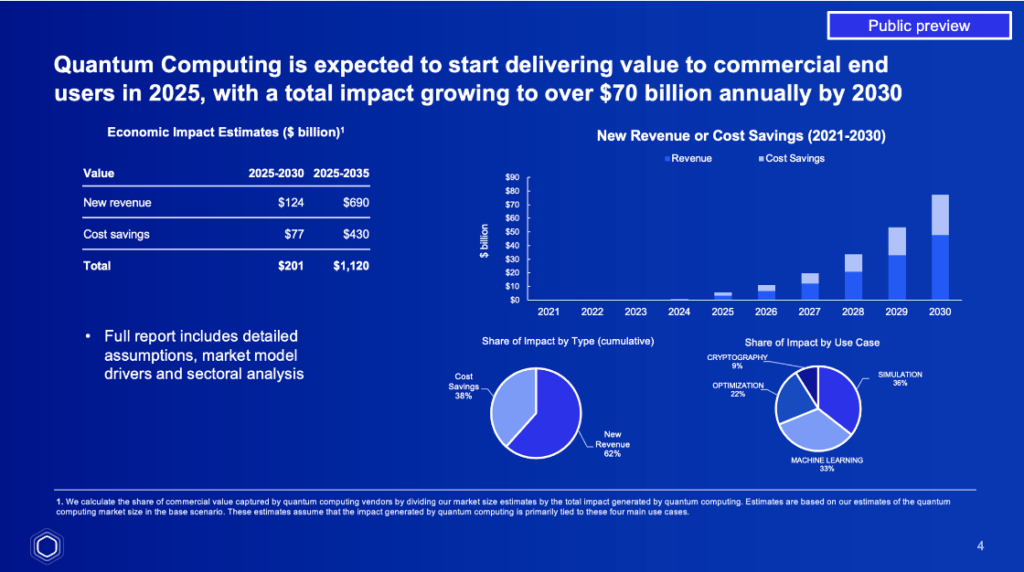

Quantum computing is expected to impact nearly every industry. Here are the major sectors experiencing early breakthroughs:
1. Medicine and Drug Discovery
Quantum computers can simulate molecules and proteins at the atomic level.
This will enable:
- Fast drug development
- New vaccines
- Personalized medicine
- Better treatment simulations
For example, researchers can simulate how a drug binds to a virus protein — something classical computers struggle to do.
2. Cybersecurity
Quantum computing is both a threat and a benefit.
The Threat
Quantum computers can break RSA and ECC encryption, which protects:
- Banking
- Military communication
- Internet traffic
The Solution
Quantum-safe cryptography is being developed to replace classical encryption.
3. Artificial Intelligence
Quantum computing will turbocharge AI by:
- Optimizing training
- Improving inference
- Enabling new machine learning algorithms
Quantum AI could make future AI systems:
- Faster
- More accurate
- More energy-efficient
4. Climate Science and Weather Prediction
Quantum computers can simulate:
- Carbon capture
- Ocean behavior
- Atmospheric chemistry
This leads to better predictions and climate solutions.
5. Finance and Investment
Financial institutions use quantum computing for:
- Portfolio optimization
- Fraud detection
- Risk modeling
- Market simulation
Complex systems that once took days will be solved in minutes.
6. Manufacturing and Engineering
Quantum simulation will help design:
- Better batteries
- Stronger alloys
- Safer aircraft
- Faster semiconductors
Quantum Algorithms: The New Era of Problem Solving
Quantum computers require specialized algorithms. Some famous ones include:
1. Shor’s Algorithm
Breaks RSA encryption — the basis of most digital security today.
2. Grover’s Algorithm
Speeds up database searching exponentially.
3. Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE)
Used for chemistry and material simulation.
4. Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA)
Solves optimization problems — perfect for finance and logistics.
Challenges of Quantum Computing


Despite the progress, quantum computing faces significant barriers.
1. Decoherence
Qubits lose quantum state very quickly — often in microseconds.
This makes long calculations difficult.
2. Noise
Environmental noise disrupts qubit behavior.
Companies must build advanced shielding and error correction systems.
3. Error Correction Complexity
Quantum error correction requires:
- Many physical qubits
- To protect one logical qubit
Example: Some systems require 1000 physical qubits to stabilize one usable qubit.
4. High Cost and Fragility
Quantum machines require:
- Specialized labs
- Cryogenic cooling
- Advanced engineering
Not something consumers will see anytime soon.
5. Lack of Skilled Quantum Developers
Quantum programming languages (like Qiskit and Cirq) require:
- Linear algebra
- Quantum physics
- Computer science
Very few people worldwide are trained in all three.
Future of Quantum Computing (2025–2035)


Experts predict massive breakthroughs in the coming decade:
1. Quantum Advantage in Real Applications
Quantum computers will outperform classical machines in:
- Weather forecasting
- Supply chain optimization
- Battery design
2. Personal Quantum Devices (Long-Term)
Not soon, but by 2040:
- Quantum chips may appear in smartphones
- Quantum sensors may become mainstream
3. Quantum Internet
Future networks will use:
- Quantum entanglement
- Quantum repeaters
For ultra-secure communication.
4. Quantum AI Systems
Artificial intelligence running on quantum hardware will be:
- More powerful
- More efficient
- More intelligent
5. More Accessible Quantum Cloud Services
Businesses will access quantum power “as a service,” paying only for usage.
Should Businesses Prepare? Absolutely.
Here’s how companies can get ready:
1. Understand Quantum Risk
Especially cybersecurity threats.
2. Explore Hybrid Quantum Solutions
Start with cloud-based tools.
3. Train Employees
Fundamentals of quantum computing will be essential in STEM careers.
4. Monitor Quantum-Safe Encryption
Soon, it will be mandatory.
5. Innovate Early
Companies that adopt quantum computing early will lead their industries.
Conclusion: Quantum Computing Is Not the Future — It Is the Present
Quantum computing is no longer hypothetical. It is advancing faster than anyone anticipated, and within this decade, it will fundamentally transform how we solve the world’s most complex problems.
It represents a once-in-a-century leap comparable to:
- The invention of electricity
- The rise of the internet
- The creation of artificial intelligence
The organizations and individuals who embrace quantum innovation today will become the leaders of tomorrow.